Written by. Ryuki Ishii based on the original Japanese article (original article’s publication date: 2022-04-08 18:05 JST)
Sega has released new supplementary materials for teaching programming to elementary, junior high, and high school students in Japan. This is a part of Sega’s Puyo Puyo Programming project, which uses the company’s iconic puzzle game Puyo Puyo’s actual source code to teach the basics of programming.
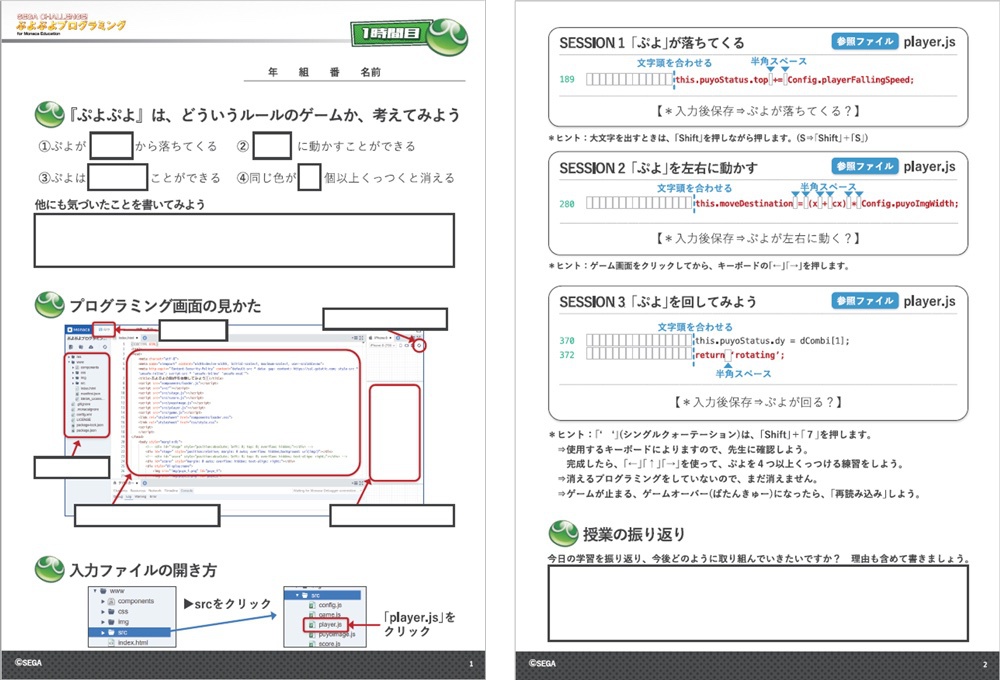
Puyo Puyo Programming initially launched in 2020 free of charge through Monaca Education, a Japanese website that provides various learning tools for coding. In addition to learning the basics of programming, users can dig deeper by modifying the source code and creating/editing/implementing images or audio files.
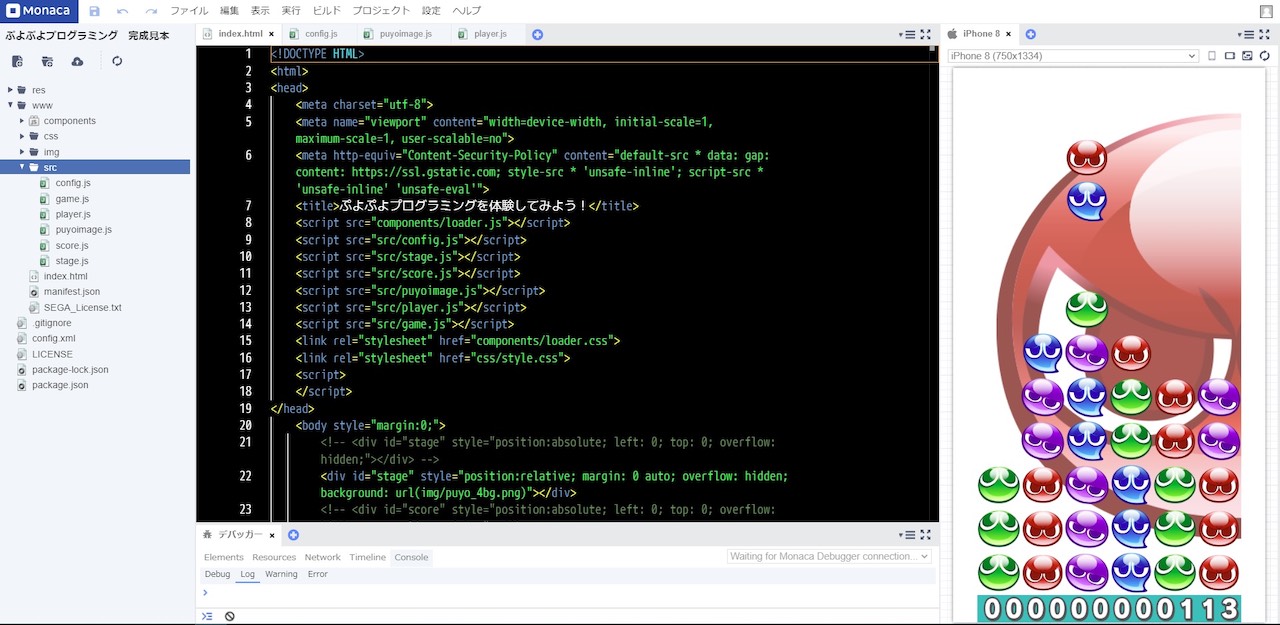
It has been used by over 100,000 users in places like elementary schools, universities, and workshops across Japan. Aomori prefecture’s Tourism and International Affairs Strategy Bureau even made a browser-based puzzle game called Puyoringo using Puyo Puyo Programming to promote the prefecture’s local specialty, Apples.
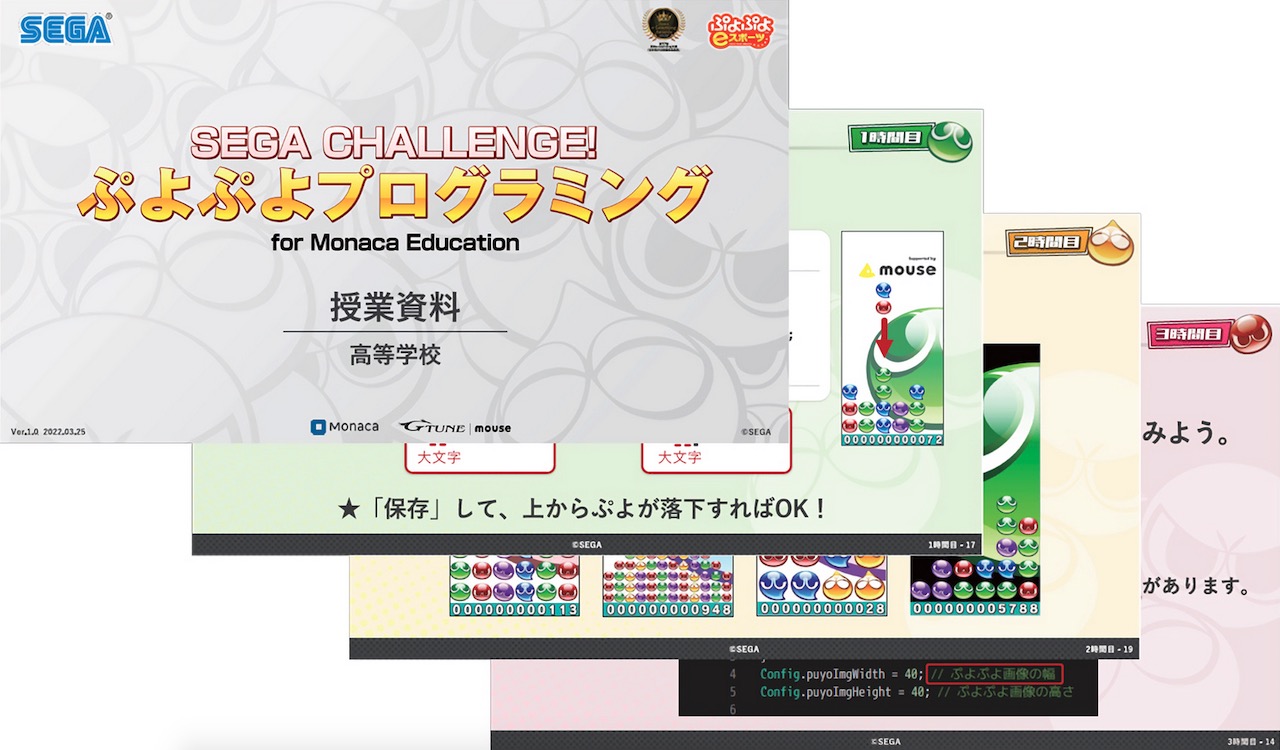
The newly released supplementary materials were supervised by Kyoto Seika University Faculty of Media Creation’s Toshiharu Kano, with an aim to make Puyo Puyo Programming more viable in schools by following the curriculum guidelines in Japan. It’s made to nurture logical thinking skills, problem-solving skills, and a better understanding of information ethics. Kano also notes that it’s a great way to develop computational thinking as well.
Programming education was first introduced to curriculum guidelines of Japan’s elementary schools in 2020, junior highs in 2021, and high schools in 2022. Sega started working on Puyo Puyo Programming as a response to these changes, with an aim to make an easy to digest learning materials that utilizing the company’s video game content. Puyo Puyo was chosen since it has a strong affinity with programming.
Sega plans to continue its efforts to provide learning materials for programming education that only a video game company like them can offer, while also taking other measures to support programming education.